Brain Surgery Using Sound Waves – Everything You Need to Know
Brain Surgery Using Sound Waves: Cerebral palsy, Parkinson’s and spinal injuries are some of the various conditions that cause uncontrollable movements known as tremors. Many take prescription medications or use other types of therapy to help reduce the symptoms. However, neurosurgeons now may also implement ultrasound brain surgery to remedy the problem.
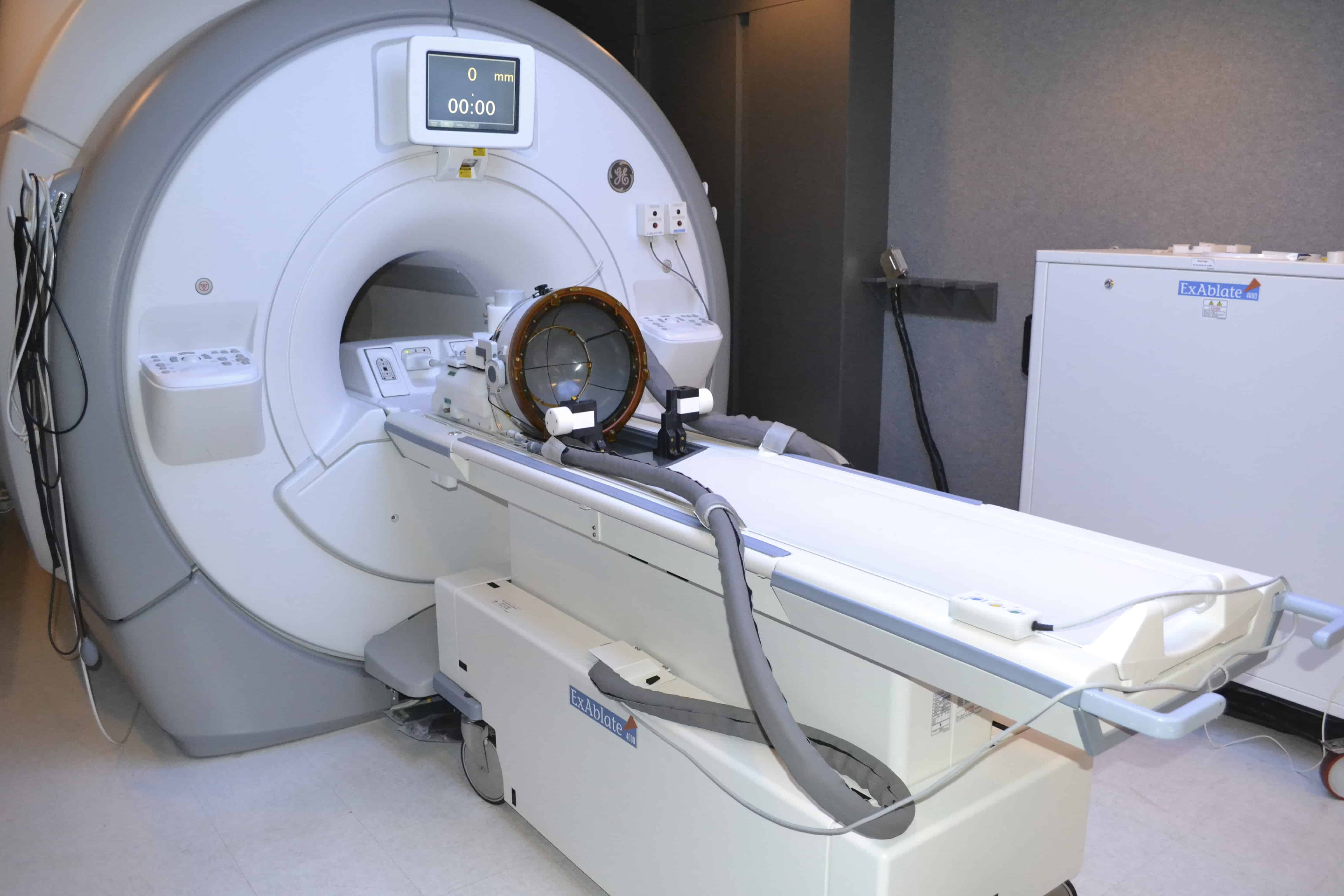
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
Many are familiar with the ultrasound technology used for diagnostic purposes. Low-intensity ultrasound does not damage tissue. However, the ultrasound equipment used for brain surgery is much more powerful. The high-intensity beams are emitted at higher frequencies than what is audible to human ears. The beam is focused on a specific target. The procedure combines ultrasound waves with MRI imaging for guidance.
Focused ultrasound was approved for the treatment of essential tremors by the FDA in 2016. European countries also received approval to perform procedures using the equipment. There are approximately two dozen focused ultrasound machines being used in the United States, Canada, Great Britain, Israel, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Spain, and Switzerland.
The Ultrasound Procedure
A patient typically undergoes MRI imaging in order for surgeons to identify the precise region requiring treatment. Using the focused ultrasound, surgeons direct three-dimensional beams to target areas measuring anywhere from 1 to 15 millimeters in diameter. The procedure begins with lower intensity waves to ensure the exact location of the waves while monitoring the toleration of the patient. The waves are gradually increased in intensity to begin the ablation process.
The individual lies on a table and wears a helmet that resembles a hairdryer from decades past. The helmet is equipped with 1,000 transducers that emit the waves. Each of the beams is weak enough that they do not harm the tissue through which they travel. However, all are directed to a focused destination where they converge to cause the ablation. The patient simultaneously undergoes MRI imaging to determine the algorithm needed to direct the beam and monitor the process.
During the procedure, patients remain awake and report that the process is painful. The procedure lasts up to five hours as the patient undergoes multiple treatments that last only a few seconds each. After each treatment, the patient is asked to speak and raise the limb affected by tremors. They might be asked to make circles with a hand, arm, foot or leg between each treatment session. In this way, surgeons determine the progress of the treatment. If a patient exhibits any abnormal speech patterns, surgeons know that the waves are affecting the wrong area.
Depending on the size of the specific area requiring treatment, the ultrasound machine may emit anywhere from 200 to 1,000 beams of focused ultrasound beams. The intensity of the sound waves effectively penetrates the skull, which negates the need to surgically remove the bone to gain access to the brain.
The high-intensity sound waves cause vibration at the molecular level, which converts the energy into heat. When the beams make contact with a single focal point, the heat produced rises up to 140 degrees Fahrenheit, which effectively destroys the targeted tissue. However, the surrounding tissue remains healthy and unaffected. By destroying the tissues, the ultrasound waves stop the abnormal signals transmitted by the neuron, which causes the essential tremors.
Living With Essential Tremors
Brain surgery for essential tremors using focused ultrasound treatment has proven an effective method of reducing uncontrollable movements, which gives the patients a better quality of life. In many cases, surgeons are able to completely eliminate tremor symptoms. The procedure is also a fraction of the cost compared to invasive conventional brain surgeries.
Patients living with spastic tremors suffer a lower quality of life. Depending on the limb affected, they may not be able to dress. Eating becomes difficult if an individual cannot hold a utensil or a glass of fluid. Some may not be able to walk or perform other normal activities of daily living. The tremors also typically worsen as the patient becomes older.
Other Focused Ultrasound Brain Surgery Applications
As of spring 2019, focused ultrasound has been used to treat more than 200,000 people around the world. According to the Focused Ultrasound Foundation, the procedure is being tested as a treatment for dozens of medical conditions. Thus far, the procedure has been used to treat malignant and benign brain tumors, depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder.






